Describe the Metabolic Response to Starvation
1 litre of oedema weighs. Main source of energy for brain.

Undernutrition Simple And Stress Starvation
Energy needs decreased as body relies on fat and protein.

. Glycogen - glucose under action of. Authors J E Schebendach 1 N H Golden M S Jacobson S Hertz I R Shenker. Loss of HMGCR compartmentalization perturbs yeast growth following glucose starvation indicating it promotes adaptive metabolic remodeling.
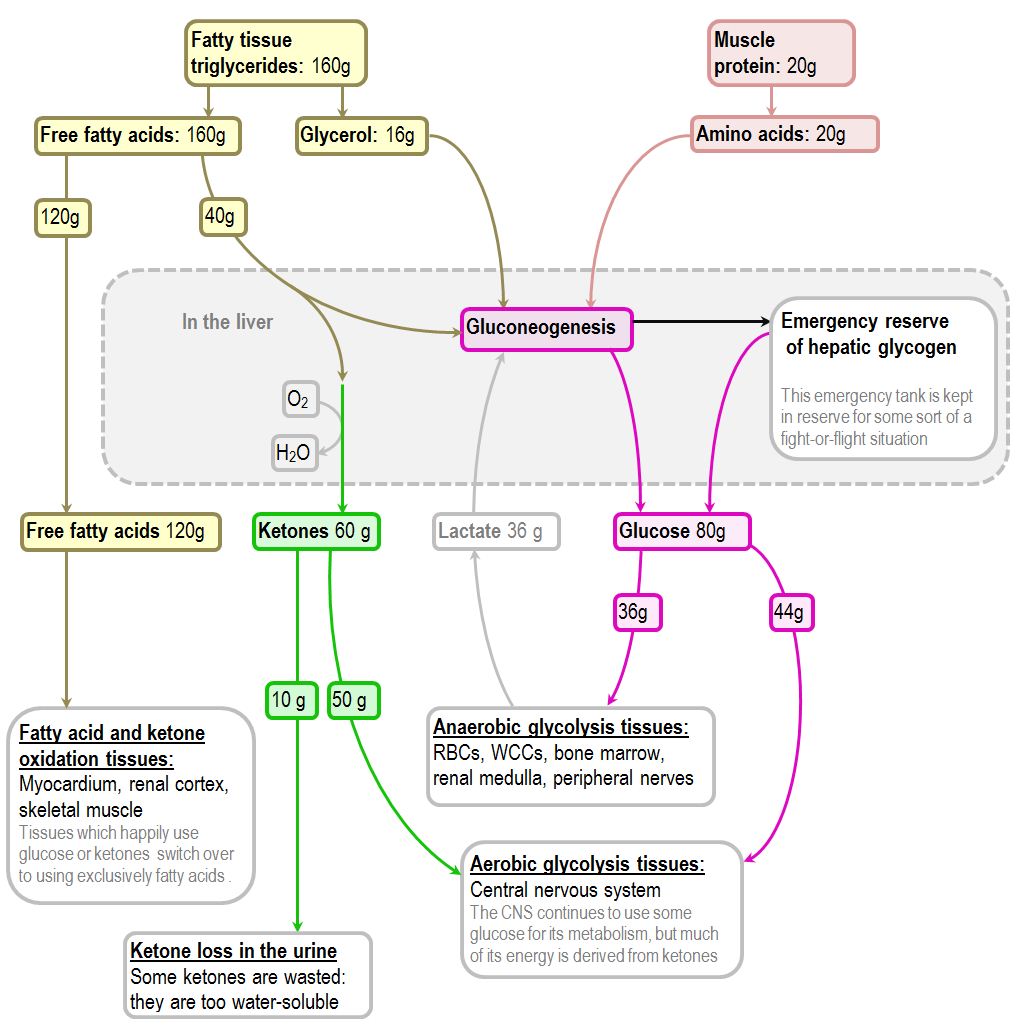
Initially stores of carbohydrate precursors eg. Ketones are produced from fatty acids. The metabolic adaptation in man to starvation semistarvation and carbohydrate restriction is complex and involves a number of hormones substrates and tissues.
The metabolic response to starvation is characterised by a switch from carbohydrate metabolism to fat cmetabolism in. 9 rows STARVATION RESPONSE. Decline in metabolic rate Refeeding syndrome involves physiologic and metabolic.
Metabolic rate following injury. - Metabolism decreases - Body lowers use of glucose to conserve it for brain and RBCs - Eventually breaks down fat -- ketones. Describe the ebb phase and flow phase of the bodys response to severe stress.
Additional MNT Considerations Short term starvation. Describe the pathway of lipid metabolism during starvation. Metabolic rate and the flexibility thereof is a complex trait involving several inter-linked variables that can influence animal energetics behavior and ultimately fitness.
Starvation Use of stored carbohydrate fat and protein to meet energy demands Liver glycogen Fatty acid stores Gluconeogenesis Glucose needed for brain and red blood cells Lean body mass protein and glycerol portion of triglycerides will be used instead. Body uses stored energy as fuel when dietary intake. 1 lipolysis is stimulated and triglycerides are converted to fatty acids and glycerol.
Starvation seriously alters the metabolic functions of our body. Equivalent or closely related terms include famine response starvation mode famine mode starvation resistance. When the data were analyzed by singular value decomposition two dominant characteristic vectors were found one corresponding to a generic starvation response and another to a nutrient-specific.
The metabolic response to prolonged starvation Early stage of prolonged starvation Starvation occurs when the body has a severe lack of nutrients needed to survive. After adipose tissue store have been exhausted. The body has ways of adapting to periods without food for example overnight it needs to survive without any additional nutrients whilst asleep.
2 fatty acids are transported to the liver and converted to ketone bodies which will be utilized by. RBCs are always dependent on glucose. High concentrations of ketone bodies result in significant excretion of ketones.
Describe the metabolic response to starvation. Metabolic response to starvation and injury. Hypothermia decreased oxygen consumption lethargy.
Metabolic traits respond readily to ambient temperature variation in some cases increasing relative or. The metabolic response to human growth hormone HGH was studied in five obese subjects in the fed state and during prolonged 5-6 wk starvation. Energy Homeostasis in your body.
In particular however the need for the ketoacids beta-hydroxybutyric acid and acetoacetic acid to replace glucose as the primary fuel for the brain of fasting man appears to be the key to maximum protein conservation. The human body switches from burning carbohydrates to fat to maintain the blood glucose levelAt the time of starvation the plasma level of fatty acids and ketone bodies increases. Starvation for a long time will cause a metabolic shift in that our body uses fat as an energy source instead of glucose.
Decreased BMR basal metabolic rate decreased activity prolonged sleep poor regulation of body temp. Affiliation 1 Eating. Degradation of muscle and organs.
Causes loss of lean body mass slightly increased proteolysis slightly increased amino acid oxidation increased gluconeogenesis mild hypoglycemia and increased lipolysis. How many days of re-feeding is required for tissue repair during the recovery phase for each day starved during the catabolic phase. Stress and energy metabolism 904.
Then in the first 24-48 hours there is increased gluconeogenesis from amino acids and glycerol. Collectively we propose a non-canonical mechanism regulating mevalonate metabolism via the spatial compartmentalization of rate-limiting HMGCR enzymes at an inter-organelle contact site. METABOLIC STRESS STARVATION What is Metabolic Stress.
During starvation most tissues utilise fatty acids andor ketone bodies to spare glucose for the brain. This metabolic arrangement must have developed under the influence of evolutionary pressure in view of the importance of protein mass for function and longevity. What are the physical effects of prolonged starvation.
Metabolic responses to starvation and feeding contribute to the invasiveness of an emerging pest insect. Mostly glucose with some ketone bodies. Metabolic responses to starvation 925.
Bodys response to metabolic stress Nutrition Diagnoses What are possible nutrition diagnoses for metabolic stress. Peripheral adipose tissue mass is only limiting when its mass is extremely small. Glucose utilisation by the brain is decreased during prolonged starvation as the brain utilises ketone bodies as the major fuel.
In the fed state three subjects HGH induced an elevation in basal serum insulin concentration a minimal increase in blood and urine ketone levels and a marked reduction in urinary nitrogen and potassium. The major metabolic responses anticipated from metabolite-specific experiments in the literature were observed as well as a number of novel responses. Metabolic responses to exercise 832.
Main source of energy. The metabolic responses to starvation and refeeding in adolescents with anorexia nervosa Ann N Y Acad Sci. Starvation response in animals including humans is a set of adaptive biochemical and physiological changes triggered by lack of food or extreme weight loss in which the body seeks to conserve energy by reducing the amount of calories it burns.
In starvation and to a lesser extent in stress starvation the loss of protein mass is spared as much as possible. What is the metabolic response to starvation. Alcohol consumption and energy metabolism 920.

Undernutrition Simple And Stress Starvation

Undernutrition Simple And Stress Starvation
Physiological Adaptation To Prolonged Starvation Deranged Physiology
No comments for "Describe the Metabolic Response to Starvation"
Post a Comment